© 2022 French-speaking Association of Readers of the Urantia Book
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Division_cellulaire
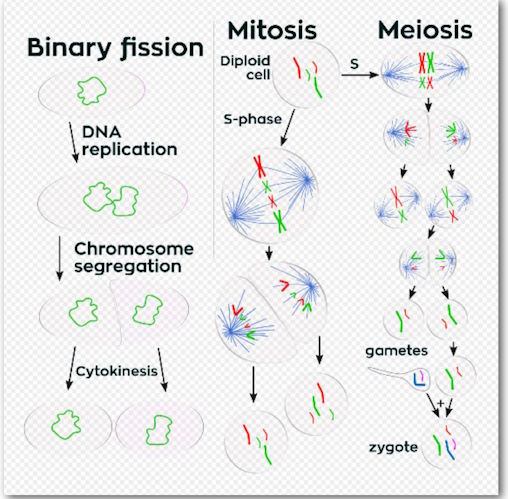
Cell division is the mode of multiplication of any cell. It allows it to divide into several cells (most often two). It is therefore a fundamental process in the living world, since it is necessary for the regeneration of any organism.
In Eukaryotes — characterized primarily by cells that have a nucleus — there are two types of cell division:
Mitosis which only allows asexual multiplication; it allows the regeneration of an organ, and also growth.
Meiosis which allows sexual reproduction.
In prokaryotes, cell division occurs by fission. These cells typically have a single chromosome that replicates before the two chromosomes move apart and the rest of the cell divides in turn.
Disorders of cell divisions can be the cause of tumors and cancers. Anarchic cell proliferation must be distinguished from normal cell regeneration. In order to understand the mechanisms underlying this division, numerous model species have been studied, including the yeasts Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, but also the embryonic development of Xenopus.